Internet of Things (IoT)
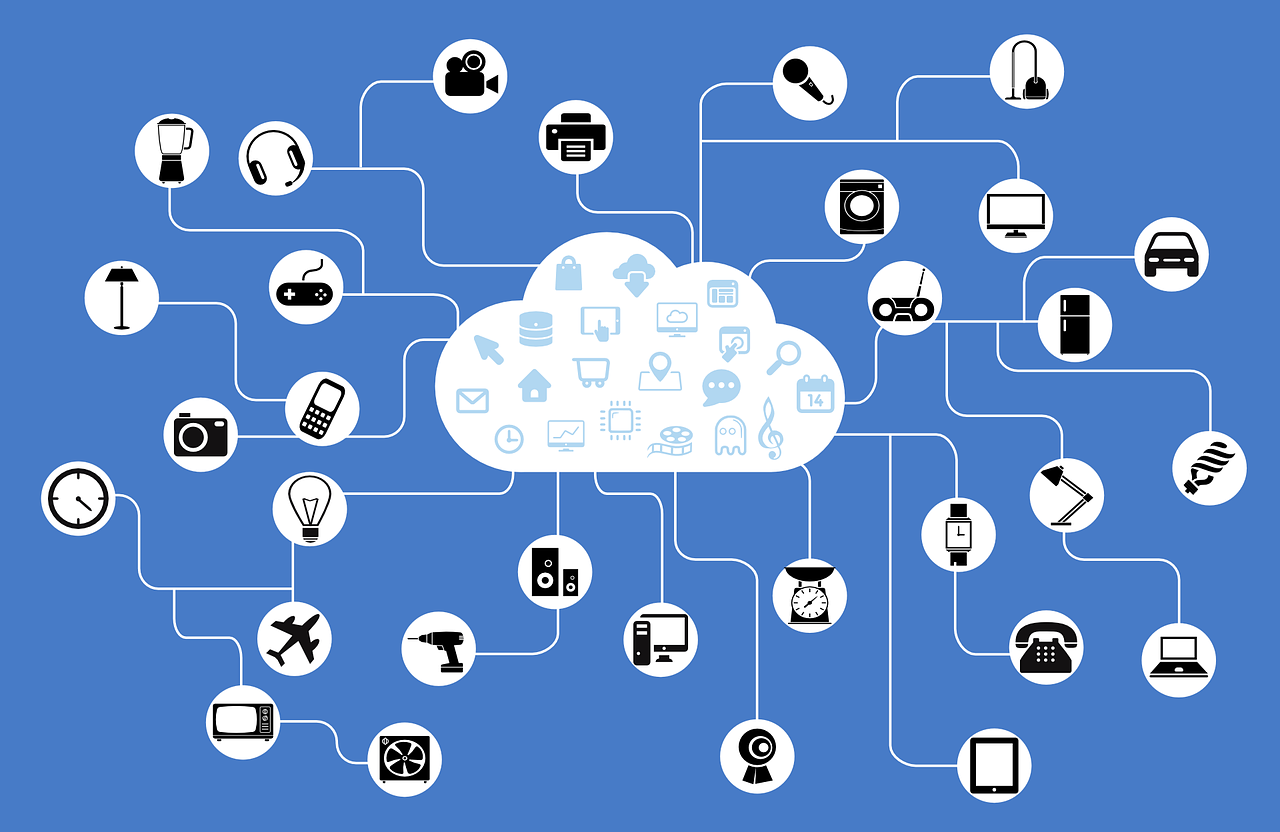
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical devices, vehicles, and other objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that enable them to collect and exchange data. This network of interconnected devices allows for the automation and remote control of various processes and systems, and has the potential to revolutionize many industries and aspects of daily life.
One of the key benefits of the IoT is that it can enable the real-time monitoring and control of various systems and processes. For example, sensors embedded in manufacturing equipment can provide data on the performance and condition of the equipment, allowing for predictive maintenance and improved efficiency. Similarly, sensors in vehicles can provide data on the vehicle's location, speed, and other factors, allowing for the development of new transportation services and applications.
The IoT also has the potential to enable new forms of communication and collaboration between people, devices, and systems. For example, connected devices in a home or office can be used to automate various tasks and processes, such as turning on lights or adjusting the temperature. In addition, the IoT can be used to facilitate communication between devices, such as allowing a person to control a device using their smartphone or other connected device.
Another important aspect of the IoT is the vast amount of data that can be generated by connected devices. This data can be used for a wide range of purposes, including improving the performance and efficiency of various systems, as well as for research and development. However, the collection and handling of this data also raises important issues around privacy and security, and there is a growing need for effective solutions to these challenges.
The IoT is still in its early stages, and there are many challenges and opportunities that need to be addressed in order to realize its full potential. One of the main challenges is the development of effective standards and protocols for communication and interoperability between different devices and systems. In addition, there is a need for more sophisticated and secure approaches to data management and analysis, as well as for the development of new technologies and applications that can take advantage of the capabilities of the IoT.
Overall, the IoT has the potential to transform many industries and aspects of daily life. By enabling the real-time monitoring and control of various systems and processes, as well as facilitating communication and collaboration between people, devices, and systems, the IoT has the potential to unlock new levels of efficiency and productivity. As the field continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and transformative applications of the IoT in the future.
The concept of the Internet of Things (IoT) was first introduced in the late 1980s, but it did not gain widespread attention until the early 2000s.
In 2004, the RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) standard was adopted as the ISO/IEC 18000 series of standards, which laid the groundwork for many IoT applications.
In 2009, the term "Internet of Things" was included in the Oxford English Dictionary.
In 2010, the number of connected devices exceeded the number of people on Earth for the first time.
In 2012, the term "Industry 4.0" was introduced to refer to the integration of the IoT into manufacturing and other industries.
In 2013, the number of connected devices on the IoT exceeded 10 billion.
In 2014, the first IoT-enabled self-driving cars were introduced.
In 2015, the term "smart cities" was introduced to refer to the use of the IoT to improve the efficiency and sustainability of urban environments.
In 2016, the first IoT-enabled smart homes were introduced.
The number of connected devices on the IoT is expected to exceed 50 billion by 2030.
Courses in computer science or information technology that cover topics such as networking, wireless communication, and sensor technology may include material on the Internet of Things (IoT).
Some universities offer specialized courses or tracks within computer science or information technology programs focused specifically on the IoT.
There may also be courses offered by online learning platforms or professional organizations that cover the topic of the IoT.
Some relevant study fields for understanding and working with the IoT include computer science, electrical engineering, information technology, and data science.



Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts. Please let me know.