What are Membership Operators in Python
What are Membership Operators in Python
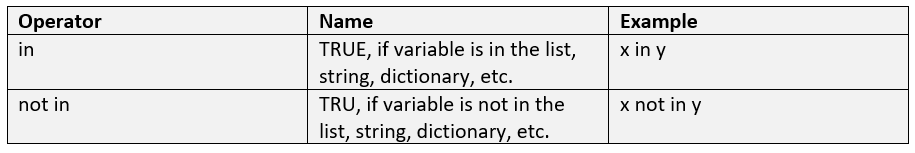
In Python, membership operators are used to test whether a value is a member of a sequence (such as a list, tuple, or string) or a set, or to test whether a value is present in a dictionary as a key. There are two membership operators in Python: in and not in.
The in operator returns True if a value is a member of a sequence or is present in a dictionary as a key, and False otherwise. For example:
Copy code
>>> colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue']
>>> 'red' in colors
True
>>> 'purple' in colors
False
>>> fruit = {'apple': 1, 'banana': 2, 'orange': 3}
>>> 'apple' in fruit
True
>>> 'pear' in fruit
False
The not in operator returns True if a value is not a member of a sequence or is not present in a dictionary as a key, and False otherwise. For example:
Copy code
>>> colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue']
>>> 'red' not in colors
False
>>> 'purple' not in colors
True
>>> fruit = {'apple': 1, 'banana': 2, 'orange': 3}
>>> 'apple' not in fruit
False
>>> 'pear' not in fruit
True
Here's an example of using the in operator to test whether a string is a substring of another string:
Copy code
>>> sentence = "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."
>>> 'fox' in sentence
True
>>> 'cat' in sentence
False
And here's an example of using the not in operator to test whether a string is not a substring of another string:
Copy code
>>> sentence = "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."
>>> 'fox' not in sentence
False
>>> 'cat' not in sentence
True
You can also use the membership operators to test whether an element is present in a set:
Copy code
>>> s = {1, 2, 3, 4}
>>> 2 in s
True
>>> 5 in s
False
>>> s = {1, 2, 3, 4}
>>> 2 not in s
False
>>> 5 not in s
True
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any questions.
Also,
Membership operators in Python are used to test whether a value or a variable is a member of a sequence (such as a string, tuple, list, set, or dictionary). There are two membership operators in Python: in and not in.
The in operator returns True if the value or variable is a member of the sequence, and False if it is not. For example:
Copy code
# Test if 'a' is a member of the string 'apple'
>>> 'a' in 'apple'
True
# Test if 'b' is a member of the string 'apple'
>>> 'b' in 'apple'
False
# Test if 'banana' is a member of the list ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
>>> 'banana' in ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
True
# Test if 'grape' is a member of the list ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
>>> 'grape' in ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
False
# Test if 'apple' is a key in the dictionary {'apple': 1, 'banana': 2, 'cherry': 3}
>>> 'apple' in {'apple': 1, 'banana': 2, 'cherry': 3}
True
# Test if 'grape' is a key in the dictionary {'apple': 1, 'banana': 2, 'cherry': 3}
>>> 'grape' in {'apple': 1, 'banana': 2, 'cherry': 3}
False
The not in operator is the negation of the in operator, and returns True if the value or variable is not a member of the sequence, and False if it is. For example:
Copy code
# Test if 'a' is not a member of the string 'apple'
>>> 'a' not in 'apple'
False
# Test if 'b' is not a member of the string 'apple'
>>> 'b' not in 'apple'
True
# Test if 'banana' is not a member of the list ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
>>> 'banana' not in ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
False
# Test if 'grape' is not a member of the list ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
>>> 'grape' not in ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
True
# Test if 'apple' is not a key in the dictionary {'apple': 1, 'banana': 2, 'cherry': 3}
>>> 'apple' not in {'apple': 1, 'banana': 2, 'cherry': 3}
False
# Test if 'grape' is not a key in the dictionary {'apple': 1, 'banana': 2, 'cherry': 3}
>>> 'grape' not in {'apple': 1, 'banana': 2, 'cherry': 3}
True



Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts. Please let me know.